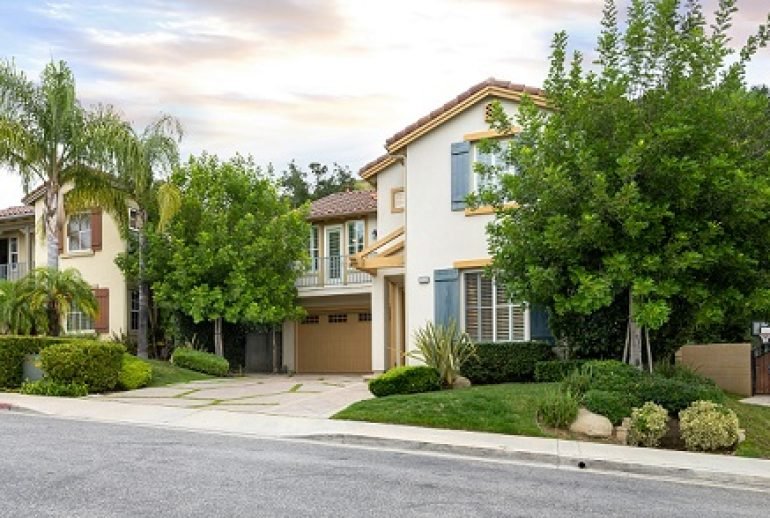
California is known for its breathtaking landscapes, booming economy, and unparalleled lifestyle. Still, one major drawback stands out: the skyrocketing cost of real estate. This raises the pressing question: why is real estate expensive in California? The answer lies in high demand, limited supply, and economic, regulatory, and environmental factors.
High Demand Drives Real Estate Costs
The sheer popularity of living in California is a primary driver of its expensive real estate. With a population nearing 40 million, the state is a hub for innovation, entertainment, and tourism. California’s cities, including Los Angeles, San Francisco, and San Diego, attract millions for career opportunities, education, and cultural diversity. This influx creates fierce competition for housing, making the demand far exceed the available supply.
Silicon Valley, the global tech capital, has contributed significantly to this trend. Thousands of workers relocate annually for lucrative tech jobs, further straining the housing market. The concentration of wealth in these areas makes properties unaffordable for many middle-income families.
Limited Land and Strict Zoning Laws
Geography plays a significant role in why real estate is expensive in California. Much of the state’s usable land is constrained by natural barriers such as mountains, deserts, and the Pacific Ocean. Urban areas, particularly those near the coast, have limited space for expansion.
Moreover, zoning laws in cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles restrict housing development. Single-family zoning, which dominates many neighborhoods, limits the number of units built on a plot of land. This keeps the housing supply low and prices high.
Regulatory and Construction Costs
California has some of the strictest regulations for housing development in the country. Environmental reviews, permitting fees, and building code requirements often lead to delays and increased developer costs. These expenses are passed on to buyers and renters, making housing unaffordable for many.
Developers also face opposition from local communities when attempting to construct affordable housing. Known as “NIMBYism” (Not In My Backyard), this resistance often slows down or halts new developments, exacerbating the housing crisis.
The Wealth Gap and Economic Growth
California’s strong economy contributes to the high cost of living. Industries such as technology, entertainment, and agriculture generate significant wealth, which is unevenly distributed. High-income earners can afford luxury properties, which inflates their overall market value. Meanwhile, middle—and low-income residents struggle to find affordable housing.
Climate and Lifestyle Appeal
Another reason Why Is Real Estate Expensive in California is its undeniable lifestyle appeal. The state’s Mediterranean climate, with mild winters and warm summers, attracts people from across the globe. Cities like Santa Monica, Malibu, and Napa Valley offer a high quality of life, scenic beauty, and proximity to beaches or vineyards, making them prime real estate locations.
However, this desirability comes at a premium. The demand for homes in such idyllic settings significantly increases property prices.
Natural Disasters and Insurance Costs
California is no stranger to natural disasters such as earthquakes, wildfires, and droughts. These events raise the cost of maintaining homes and infrastructure. Homeowners often face higher insurance premiums, adding to the overall expense of owning property in the state.
Case Study: Housing Prices in San Francisco
San Francisco provides a clear example of the challenges facing California’s real estate market. The city has one of the highest median home prices in the country, surpassing $1.2 million as of 2023. The combination of limited land, stringent zoning, and high demand from tech workers has created an almost unattainable housing market for most residents.
Efforts to address this issue, such as building more affordable housing, have faced significant resistance from local stakeholders. As a result, many residents are forced to relocate to neighboring regions or even out of state.
Why Housing Costs Continue to Rise
The following factors summarize why housing prices in California remain on an upward trajectory:
- Population Growth: California’s population growth continually increases the demand for housing.
- Limited Development: Strict zoning laws and geographic constraints restrict the supply of new homes.
- High Development Costs: Regulatory expenses and community opposition hinder affordable housing projects.
- Economic Disparity: Wealth concentration in urban areas inflates property prices.
Potential Solutions to California’s Housing Crisis
To address why real estate is expensive in California, several solutions have been proposed:
- Relax Zoning Restrictions: Allowing multi-family housing in single-family zones could increase supply.
- Streamline Permitting: Simplifying the construction approval process can reduce development costs.
- Invest in Affordable Housing: Public and private initiatives can support the construction of low-cost homes.
- Encourage Suburban Growth: Expanding public transportation can make suburban living more accessible, reducing demand in crowded urban areas.
Conclusion
So, why is real estate expensive in California? The answer lies in a complex interplay of factors: high demand, limited land availability, stringent regulations, and the state’s lifestyle appeal. While solutions such as zoning reforms and affordable housing investments show promise, the path to resolving California’s housing crisis will require collaboration between policymakers, developers, and residents.
Understanding the reasons behind California’s expensive real estate market highlights the need for innovative strategies to balance growth with affordability, ensuring that the Golden State remains where everyone can find a home.
- How to Get Mildew Smell Out of Rug: Complete Guide - May 11, 2025
- Overcoming Language Barriers in French Business Settings - May 5, 2025
- Interior Design Consultants for Stylish and Personalized Interiors Tucson - January 14, 2025